Ginkgo: A High-Performance Portable Numerical Linear Algebra Software
Monday, May 22, 2023 3:00 PM to Wednesday, May 24, 2023 5:00 PM · 2 days 2 hr. (Europe/Berlin)
Foyer D-G - 2nd Floor
Research Poster
Emerging HPC Processors and AcceleratorsExascale SystemsMixed Precision AlgorithmsNumerical Libraries
Information
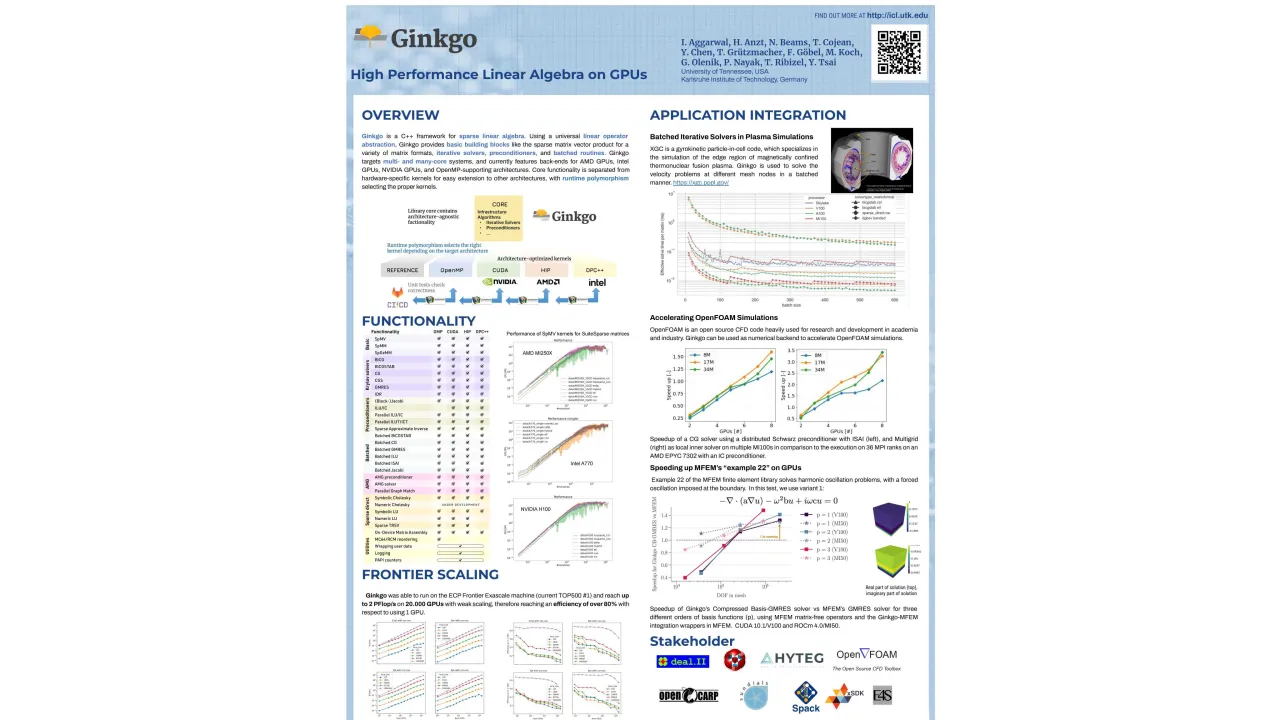
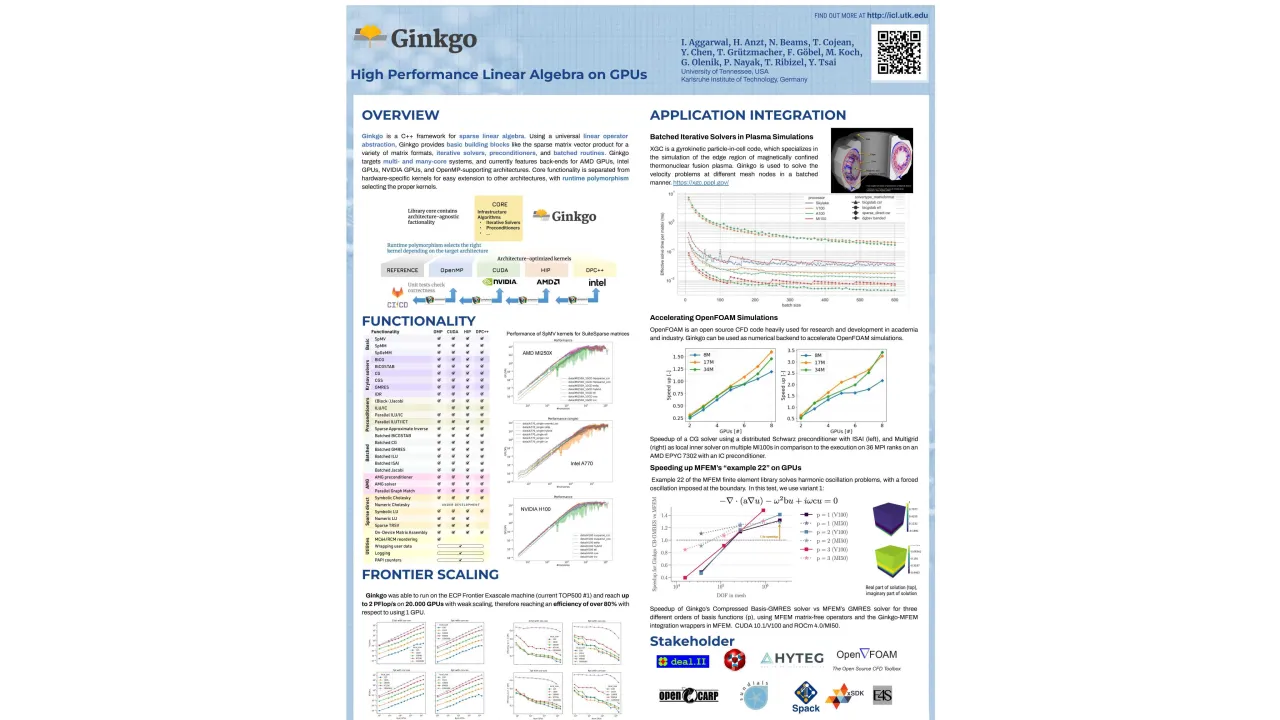
Numerical linear algebra building blocks are used in many modern scientific applications codes. Ginkgo is an open-source numerical linear algebra software that is designed around the principles of portability, flexibility, usability, and performance. The Ginkgo library is integrated into the deal.II, MFEM, OpenFOAM, HYTEG, Sundials, XGC, HiOp, and OpenCARP scientific applications, ranging from finite element libraries to CFD, power grid optimization, and heart simulations. The Ginkgo library grew from a math library supporting CPUs and NVIDIA GPUs to an ecosystem that has native support for GPU architectures from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel, can scale up to hundreds of GPU. One of the keys to this success is the rapid development and availability of new algorithmic functionalities in the Ginkgo library such as, but not limited to, Multigrid preconditioner, advanced mixed-precision iterative solvers and preconditioners, a sparse iterative batched functionality, sparse direct solvers, and the distributed MPI-based backend. In this poster, we present the Ginkgo library, its design as well as its performance, and several application use cases. Ginkgo's approach to a simple yet uniform C++ interface could be of interest to other framework developers. The portability approach through a backend system allowing both high-performance vendor-specialized kernels and portability is relevant to all other HPC application developers who face a similar design choice. The goal of this poster is to stimulate discussion with application developers who could benefit from the advanced features present within the Ginkgo library in order to accelerate their problems on distributed, multi-GPU systems.
Contributors:
Contributors:
Format
On-site
Beginner Level
50%
Intermediate Level
40%
Advanced Level
10%

